Page Contents
What is Height-to-Waist Ratio (HtWR)?
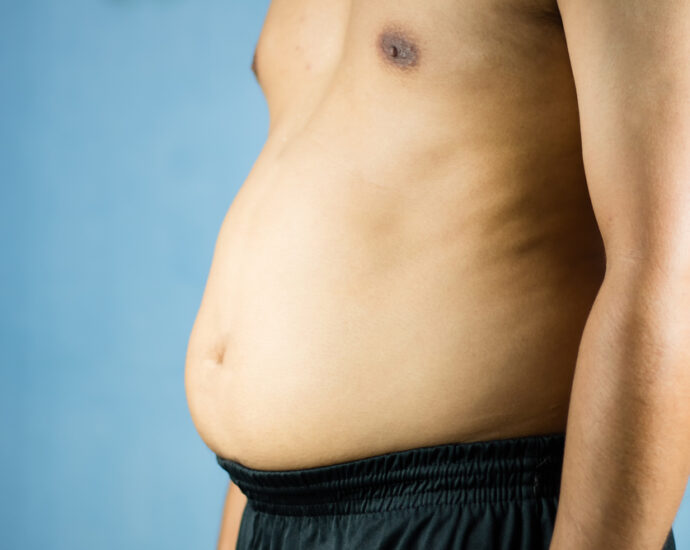
The height-to-waist ratio (HtWR), also called the waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), is a simple but powerful health metric that compares the circumference of your waist to your height. This ratio is increasingly recognized as a more accurate predictor of health risks—such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and premature death—than traditional measures like Body Mass Index (BMI).
Why It Matters More Than BMI
BMI has long been the standard for evaluating healthy weight, but it has significant limitations. BMI does not account for muscle mass, bone density, or fat distribution. Two individuals with the same BMI can have vastly different health profiles, especially if one carries more visceral fat—the type of fat stored around abdominal organs.
HtWR, on the other hand, focuses on central obesity, which is a stronger predictor of chronic diseases. Since abdominal fat is metabolically active and linked to inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular problems, knowing your waist size in relation to your height provides critical insight into your health risks.
How to Calculate Your Height-to-Waist Ratio
Calculating your HtWR is simple:
- Measure your waist: Use a tape measure to measure the smallest point around your abdomen, usually just above the belly button. Do this while standing, relaxed, and breathing normally.
- Measure your height: Stand straight without shoes and measure from the floor to the top of your head.
- Use the formula: Divide your waist circumference by your height.
Make sure both measurements are in the same units (inches or centimeters).
Interpreting the Results
The general guideline for a healthy waist-to-height ratio is:
- Men: HtWR should be less than 0.53
- Women: HtWR should be less than 0.50
- A HtWR over 0.60 is considered dangerously high and associated with increased health risks
These benchmarks may vary slightly across studies, but the consensus is clear: keeping your waist circumference less than half your height is a good rule of thumb for health.
Health Risks of a High Height-to-Waist Ratio
If your HtWR is too high, it may indicate excessive visceral fat, which is associated with:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Stroke
- Sleep apnea
- Hypertension
- Certain cancers (e.g., breast, colon)
- Early mortality
Advantages of Using HtWR
- Gender-neutral and age-independent: Unlike BMI, HtWR works across different age groups and body types.
- Early warning: It can detect risk in individuals with a “normal” BMI who still carry dangerous belly fat.
- Ease of use: Requires only a tape measure—no scales or special equipment needed.
- Actionable insights: Encourages fat loss from the midsection, which has the greatest impact on health.
Tips for Improving Your Height-to-Waist Ratio
Improving your HtWR is about reducing abdominal fat, and that comes down to:
- Nutrition: Emphasize whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and limit processed sugars and refined carbs.
- Exercise: Combine aerobic activity (like walking, running, or swimming) with strength training.
- Sleep and stress: Poor sleep and chronic stress can increase abdominal fat.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking: Both contribute to increased waist circumference.
Final Thoughts
The height-to-waist ratio is a low-cost, easy-to-understand tool that can give you powerful insights into your health. Unlike BMI, it focuses on where fat is stored—an essential factor in determining your risk of serious diseases. Monitoring and maintaining a healthy HtWR can guide lifestyle changes and ultimately lead to a longer, healthier life.
READ MORE: Eat These Foods To Burn Belly Fat
Sources:
https://healthsurgeon.com/calculate/waist-height-ratio/
https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/measuring-your-waist
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5118501/