Erythroderma treatment is vital when a person suffers from erythrodermic psoriasis, a rare but very serious type of psoriasis.
Page Contents
Why is erythrodermic psoriasis a serious condition?
In this skin disease, the patient has widespread, fiery, burning skin that is itchy and painful. Some risk factors increase the chance of this chronic skin condition.
The doctor treats the autoimmune disease through a variety of options, although combinations of treatments may be needed to control the disease. The treatment is usually successful, but occasionally a patient can no longer be helped and dies as a result of complications such as heart failure, pneumonia, or sepsis (blood poisoning).
Addressing risk factors lowers the chances of getting this aggressive type of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. This occurs when the body’s natural defense system attacks healthy tissue.
At the time of writing, it is still unknown what the exact cause of the chronic skin disease is.
Overproduction of T cells occurs in patients with psoriasis. These are a type of white blood cell that ward off bacteria and viruses. In psoriasis, these T cells attack healthy skin cells. A variety of symptoms arise due to the increase in skin cells and T cells.
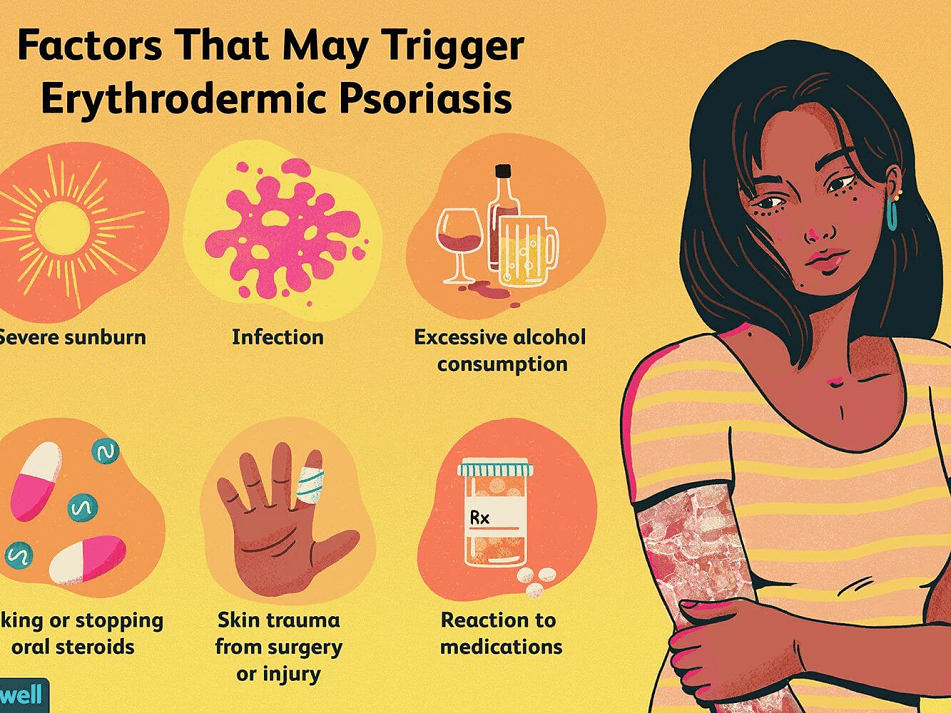
Risk factors of erythrodermic psoriasis
In general, most types of psoriasis are the result of the same triggering factors:
- alcohol abuse
- allergies such as an allergic reaction to a medication
- a skin lesion
- an infection such as HIV infection
- severe sunburn
- medicines such as lithium, antimalarials, corticosteroids, or strong coal tar products
- suddenly stopping systemic psoriasis treatment
- difficult to treat psoriasis – erythrodermic psoriasis also sometimes occurs when
- psoriasis (especially plaque psoriasis) is difficult to control
- stress
- nutrition
- weather
Symptoms of Erythrodermic Psoriasis
The symptoms develop gradually or suddenly.
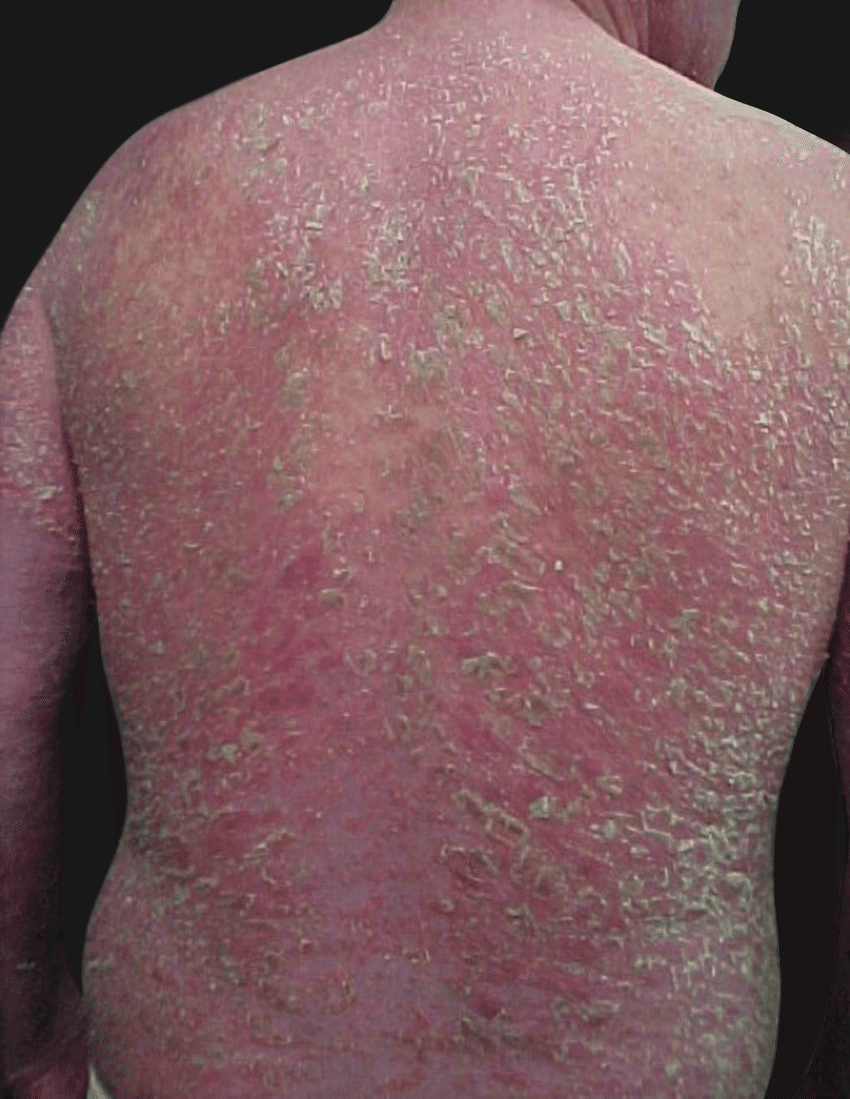
In erythrodermic psoriasis, the patient has a widespread rash that covers most or even the entire body. The rash consists of red, scaly patches often with severe itching and pain. The fiery, red skin appears burnt.
The autoimmune condition even causes peeling of the skin in large sheets. There may also be pustules that are filled with pus.
Other symptoms are
- a high heart rate
- a quick pulse
- joint pain
- swollen ankles
- fever
- chills
- muscle weakness
- changes in body temperature such as hypothermia because the patient cannot keep himself warm
- circulatory disturbances
If the patient has these symptoms, he should see the doctor immediately.
Diagnosing Psoriatic Erythroderma
The doctor questions the patient about his medical history. The doctor also wants information about a family history of psoriasis.
He also checks for possible risk factors such as taking corticosteroids by mouth, the presence of an infection, or suddenly stopping taking psoriasis medications.
Next, a physical exam is needed where the doctor looks for the presence of some psoriasis signs such as plaques on the skin, joint pain, and nail psoriasis.
The doctor will perform a skin biopsy in which he removes a piece of the affected skin and has it checked in the lab for signs of psoriasis.
There is no laboratory test to confirm that the patient has erythrodermic psoriasis, but laboratory tests can rule out other causes of similar symptoms, such as atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and other conditions.
Erythroderma Treatment
The symptoms of this disease are not always easy to treat.
The patient may need to try multiple treatments or combinations of treatments before symptoms can be controlled.
Treating erythrodermic psoriasis
Exfoliative psoriasis should not be underestimated because of its dangerous and life-threatening complications. Those affected should go to the hospital as soon as possible if symptoms occur.
This is the only way to alleviate symptoms to prevent a worse fate. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, the therapy can be complicated and time-consuming.
The symptoms of this disease are not easy to treat. The patient may need to try multiple treatments or combinations of treatments before symptoms can be controlled.
Most of the time treatment works well. There are times however when the condition results in death. Deaths that do occur are generally related to infections such as pneumonia and staphylococcal septicemia.
1. Topical treatment for erythrodermic psoriasis
The doctor treats the autoimmune disease through a variety of options, although combinations of treatments may be needed to control the disease.
Basically, it is important during therapy to sufficiently moisturize the skin, inhibit inflammation, and to effectively relieve the intense itching.
The following measures are taken:
- Steroid and moisturizing creams
- Moist wraps
- Baths with oatmeal
2. Systemic therapy for erythrodermic psoriasis
Systemic therapy is carried out by taking the following active ingredients orally:
- Acitretin
- Cyclosporine
- Infliximab
- Methotrexate or
- Biologics
Because of the often severe pain, painkillers are often given as part and parcel of erythroderma treatment. Antibiotics are also a necessary treatment for this disease. They are used to treat existing infections or to avert them timeously.
Exfoliative erythrodermic psoriasis often results in critical protein loss in the skin. Those persons affected are therefore often prescribed a psoriasis diet high in protein to compensate for the deficiency.
While most patients with erythrodermic psoriasis do well after one or more treatment options, it is not possible to help some patients.
The condition sometimes leads to death.
Complications from the erythrodermic psoriasis skin condition
The skin is important to your overall health. It helps regulate body temperature, keeps germs and toxins (poisons) out, and retains moisture.
Erythrodermic psoriasis affects these functions and sometimes causes life-threatening complications.
For example, the patient has to deal with dangerously low body temperature (hypothermia), the loss of much-needed proteins and fluids, and serious illnesses such as sepsis (blood poisoning) and pneumonia.
If a patient loses too much fluid, the heart will not have enough blood to pump. That leads to shock, kidney failure, and heart failure.
Conclusion
Erythrodermic Psoriasis – The most serious form of psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a rare and dangerous exception between all the comparatively harmless forms of psoriasis. If you fail to notice your body’s signals in good time, it can have serious and life-threatening consequences.
As a person with psoriasis, it is important to know the possible triggers and risk factors of this disease and to avoid them at all costs.
Above all, this means that you always adhere to the psoriasis routine prescribed by your doctor and do not discontinue treatment without a valid reason.
It is also important to consult a doctor or hospital immediately if symptoms arise or if you suspect anything.