Page Contents
What is sinus congestion?
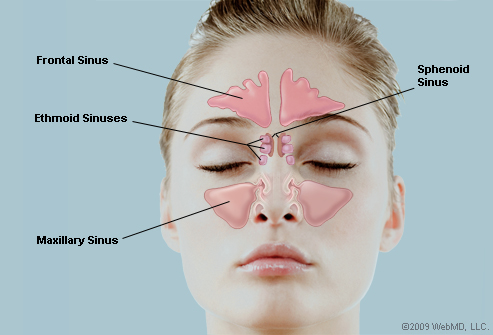
Sinuses are hollow air-filled cavities in the skull. Under normal circumstances, these cavities are all open to the nasal airway by means of an ostium, which is a narrow opening in the bone.
All humans have 4 pairs of these cavities which are situated in the bones of the face as follows:
- frontal sinuses: above the eyes in the middle of each eyebrow
- maxillary sinuses: in the cheekbones on either side of the nose
- ethmoid sinuses: behind the bridge of the nose between the eyes
- sphenoid sinuses: behind the ethmoid sinuses and behind the eyes
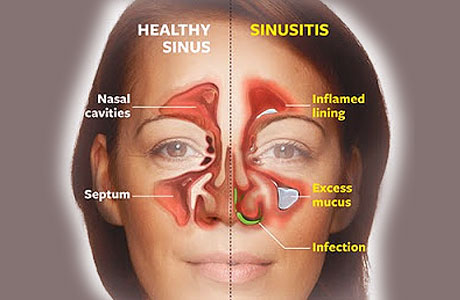
The normal condition of sinuses, as mentioned earlier, is to be filled with air. Sinuses have a thin layer of soft, pink tissue called mucosa (mucous membrane) which helps to keep the inside of the nose moist. Blocked sinuses occur when these sinus linings (tissues) become swollen due to allergens, pollutants and dust which cause sinus passages to be filled with fluid; creating the ideal environment for the growth of bacteria, viruses and germs, causing sinusitis (inflammation of sinuses). Sinus congestion is thus blocked sinuses or sinusitis.
What is sinus congestion causes:
- Viruses: colds are responsible for most sinus infections. Colds cause nasal tissue to swell which block those holes which drain sinuses
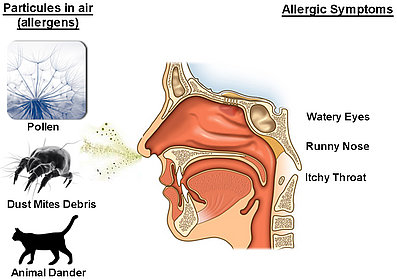
- Allergies: those people who are prone to hay fever or allergies should avoid triggers like pet dander, mold, dust mites, etc.
- Bacteria: most likely those known as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenza
- Polyps: are small harmless growths. Polyps originate from sinus tissues. They prevent mucus from being drained, causing sinus cavities to become blocked and infected. Headaches can be triggered when the polyps restrict airway passages.
- Pollutants: from strong odors such as perfumes, dust and air pollution can contribute to irritate the nose, coughing and bring about inflammation which in turn may lead to sinusitis

- Swimming for persons susceptible to sinus infection should be limited to short periods in the water as chlorine may irritate the nasal tissue and sinuses
- Diving: the pressure from diving may cause water to be pushed into the sinuses and cause irritation and inflammation of the tissue
- Flying may irritate the sinuses. Pressure can build up in your head when the in-flight pressure is reduced, leading to possible blockage of sinuses and air passages, provoking cold symptoms.

- Fungi are considered unusual triggers of sinus infection. When it is however the cause of sinus infection, it is most commonly found in individuals who have a compromised immune system. A weakened immune system is more susceptible to fungi growth, especially in dark and damp environments such as the sinuses. Aspergillus is the fungus generally associated with sinusitis.
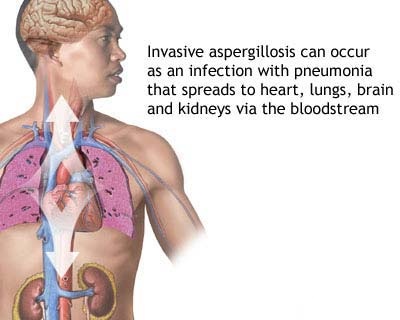
- Smoke of cigars and cigarettes cause irritation to the nose of most people (myself included). The irritation may lead to inflammation which makes people more prone to infection of the sinuses. This obviously puts smokers at greater risk as the continuous smoking damages the sinus-cleaning system. Lack of moisture and dry air in the nasal passages make the development of sinusitis thus more likely. Keep your nose moist by drinking lots of water, by avoiding caffeine and by using a humidifier during the winter months.

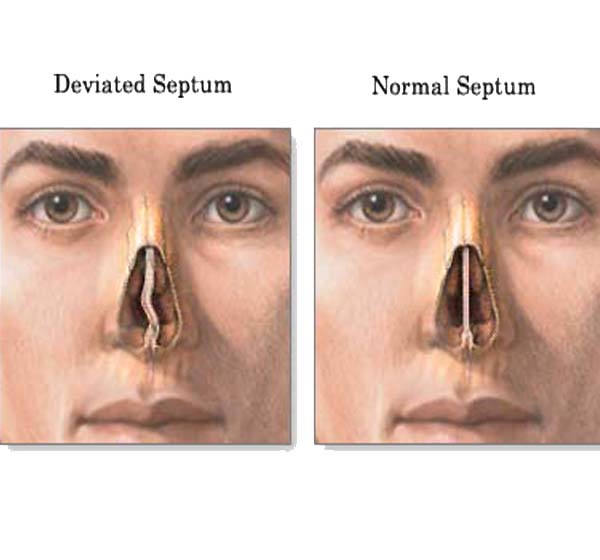
- Abnormalities such as a deviated septum (a shift in the nose’s center section to one side; often the cause of chronic sinus infection), tumors, narrow drainage passages, a cleft palate, a chronic condition such as cystic fibrosis and enlarged adenoids (masses of tissue in the passage between the nasal cavity and the throat) can all greatly prevent the drainage of mucus. This leads to inflammation of the nasal passages and thick mucus developing; setting the stage for the onset of sinusitis.
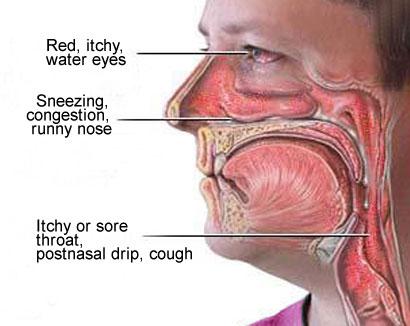
What is sinus congestion symptoms:
- Pain: as mucus accumulate in blocked nasal passages, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the face sets in. Pain is usually experienced in the forehead, in the upper jaws and teeth, between the eyes or on either side of the nose. Pain in ears due to pressure is often experienced.
- Sinus discharge: from either the nasal passages or flowing down your throat may be yellow or green and comes from infected sinuses. When it tickles the throat it’s called a postnasal drip.
- Headache: blocked sinuses and inflammation cause muscles in the forehead to tighten, leading to headache
- Stuffy nose: is probably one of the most prevalent signs of sinusitis. As a clogged nose is also symptomatic of the common cold, the duration of the symptom is the differentiating factor: stuffy nose symptom lasts longer when it’s a sinus infection

- Bad breath (halitosis) is the smell caused by the by-products which is produced by the organisms which cause the infection; emanates from the discharge which collects in the nose and sinuses and drips into the throat
- Coughing up phlegm is symptomatic of both colds and bronchitis also. With sinusitis however, the coughing generally is a lot worse at night and in the morning. Sinuses drain into the throat when you lie down; when you get up, it comes up and drains out of the throat.
- Sore throat: sinus congestion and sore throat often goes hand in hand. Postnasal drips may leave a person with a raw and hurting throat when the infection lasts for weeks. The dripping mucus irritates and inflames the throat, causing a sore throat.
- Fever is not usually a symptom of sinus congestion; sinus infection can however result in a fever, which incidentally, if it gets worse, means you need some medical attention.

- Hurting teeth is not actual toothache, but sinus infection can feel like toothache. It is however referred pain from the pressure which is building up in the head, and usually presents itself on both sides of the face.
- Diminished sense of smell and taste: these senses normally work when air movement in the sinuses gives a signal to your brain, thus letting you know what you’re smelling or tasting. Once again, the inflammation which prevents the sinuses from draining is the reason why these senses become dull.
Different types of sinusitis:
- Acute sinusitis: on average lasts up to 4 weeks and starts suddenly with cold-like symptoms like a runny and stuffy nose, accompanied by facial pain that remains for longer than 14 days.
- Subacute sinusitis: is inflammation which last between 4 to 8 weeks.
- Chronic sinusitis: is a condition where the sinus inflammation symptoms usually last for 8 weeks and longer.
- Recurrent sinusitis: is characterized by several attacks in the span of 1 year.
When to see a doctor
Can sinus infection go away on its own? Yes, but you need to seek medical attention when
- your symptoms do not clear up in 10 days
- symptoms last for many weeks and keep on coming back
- You run a fever (while not impossible, fever is not a typical symptom of sinusitis. An underlying condition may be the cause of your sinus infection)
- headaches do not let up with over-the-counter pain relief medication
In conclusion:
In the event you feel uncertain about your health in any way, best consult a doctor. Though not the norm; untreated sinus infections may cause damage to the sinuses which could lead to more serious conditions such as ear infections, chronic sinusitis, vision loss or heaven forbid, meningitis (a serious disease in which there is inflammation of the meninges, caused by viral or bacterial infection, and marked by intense headache and fever, sensitivity to light, and muscular rigidity).